2022 – Reports | SDG 13 – Climate Action

Low Carbon Energy Use
Installation of 20kW Roof-mounted Grid-tied Photovoltaic System at the Climate Change Building, ISU Echague Main Campus
In view of the measurement of the amount of low carbon energy used across the university, a 20-kW roof-mounted grid-tied photovoltaic system (GTPVS) installed at the Climate Change Center building at Isabela State University, Echague Campus was assessed in terms of its actual power generated, grid power and electric bill reduction and contribution to climate change mitigation.
Running power from an ordinary electricity meter was 0.4 kW/sec. Input current and voltage with running heavy load equipment (5 tonner aircon, 600 watts server and workstations) were 40.5-98.8 A and 234-235 V, respectively, yielding 9.5-23.12 kW power range. Daily generation power ranged between 5 and 10 kW from 7am to 3pm. Daily exported power reached as high as 30 kW. Exported energy was highest in 2019 at 70 MWh that was dumped to avoid added kWh readings payable by the University. Electric consumption ranged from 1,011 kwh in January 2020 (cold season) to 2,562 kwh in April 2019 (summer season). Indicative electric bill reduction was P32,677 from 4,736 to 1,237 kWh power reduction.
In relation to this, an electric bill reduction was observed based on the records of electric bills before and after the installation of the roof mounted GTPVS. The power consumption was reduced from 4,736 kWh (17.05GJ) to 1,237 kWh (4.45 GJ). Thus, the proportion of energy from the 20kW GTPVS as a low-carbon source was 26.10%.
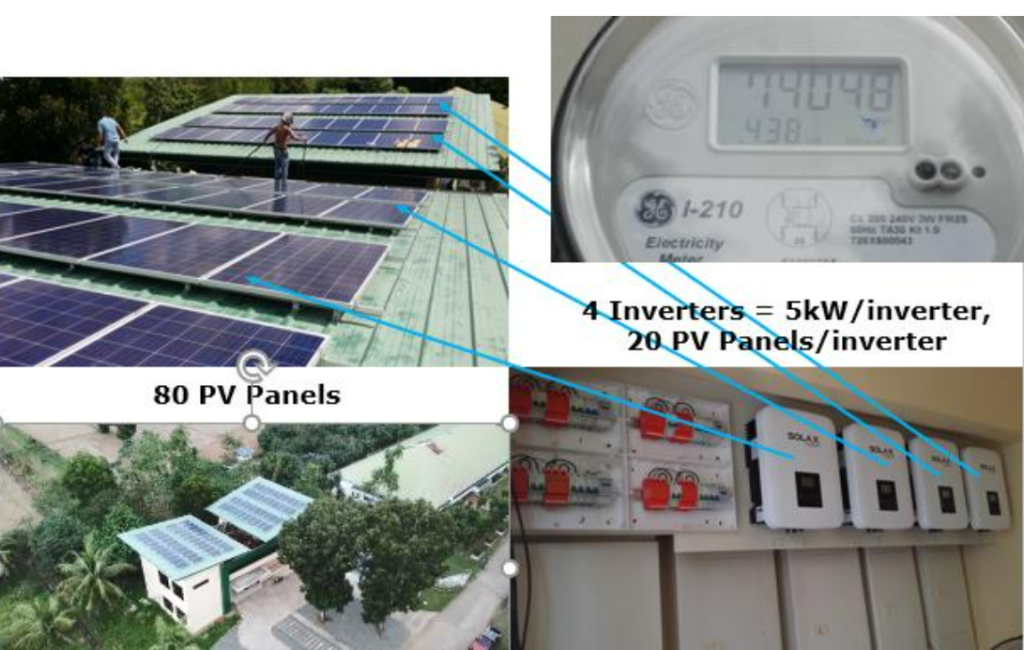

Roof-mounted photovoltaic system of the climate change center building comprising 80 solar/PV panels and four5-kW inverters connected to the main circuit.
Environmental education measures
Subjects offered in view of Climate Change Awareness and Disaster Risk Management
Institutional subjects such as Climate Change Adaptation-Disaster Risk Management (CCA-DRM) taken by all students in all degree programs both in undergraduate and graduate levels started in 2014, and Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction Management (CCDRRM), offered during the first or second semester in the first academic year. These subjects provide necessary concepts, principles, historical data and latest scientific developments on climate change and study of disasters.
Tree Planting Activities
In view of the National Environmental Awareness Month last November 2022, the officers of Supreme Student Council of ISU-Cauayan Campus initiated a Tree Planting event which was participated by the students from different colleges and departments. ISU-San Mateo Campus also conducted the same activity through their Adopt-a-Barangay extension project.
This kind of activities will indeed spread awareness and cautiousness among students and communities in taking care of the environment through the important function of forest trees in climate change adaptation such as windbreakers, landslide and soil erosion control, as well as sequestering carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas in the atmosphere as a significant climate change mitigation strategy.
Students’ Awareness on Environmental Concerns and Management and Protection Strategies: A Baseline Framework for the Development
This study was conducted to determine the level of awareness of the students at Isabela State University, City of Ilagan Campus on environmental concerns and management and protection strategies. It aims to gather baseline data to come up with a framework for the development of a responsive culture on climate change.
The study revealed that most of the respondents are female and are in curriculum year level II. The respondents, although they are fully aware of some environmental concerns as well as environmental protection strategies, like waste management, pollution control, reforestation, and organic farming to mitigate climate change, their baseline knowledge on the several other environmental concerns and management and protection strategies could still be improved, specifically on genetic engineering and acid rain.
A massive educational and information dissemination campaign could be conducted to raise the awareness of the students on several other environmental concerns and protection strategies that they are not yet fully aware of. The baseline data to come up with a framework for the development of a responsive culture on climate change has been gathered. A follow-up study on the instructional integration of environmental concerns and management, environmental protection strategies, as well as risk reduction management, is in place.
Trainings conducted on Climate Change Awareness and Disaster Risk Assessment
On December 5 to 7, 2022, the Department of Human Settlements and Urban Development (DHSUD), through the leadership of Regional Director Peter Daniel G. Fraginal and ELUPDD OIC-Chief, Engr. Perlita B. Calubaquib, facilitates the Training on Climate and Disaster Risk Assessment (CDRA) Mainstreaming at Go Hotels, Tuguegarao City.
The activity was attended by the Local Planning Teams of the Municipalities of Aparri, Amulung, Calayan, Gattaran, Echague and the City of Ilagan. Personnel from the Provincial Planning and Development Office of Nueva Vizcaya and Quirino likewise attended through virtual means.
The activity was conducted to assist Local Government Units in introducing Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction measures in the updating of their Comprehensive Land Use Plans and other local development plans.
Similar activities will be conducted in the year 2023 for other LGUs.

Environmental Scientist Bondee Penaflor of the Isabela State University and HHRO I Angerreyfie C. Masinas & HHRO III Mohammad Haydrey K. Animulla of the Monitoring and Evaluation Division of the Environmental, Land Use and Urban Planning and Development Bureau of DHSUD discussing the CDRA processes.
On the other hand, in 2003, the Cagayan Valley Regional Geographic Information Network (RGIN) was created through RDC 2 Resolution No. 02-23-2003. The network was established basically with the following functions:
- Establish a collaborative network of regional and provincial GIS centers;
- Facilitate and promote the utilization and application of GIS technology in planning, programming and project development, monitoring and evaluation, consistent with ecologically sound conservative principles;
- Provide RLAs, LGUs and Civil Society Organization with accurate and up-to-date information for policy making, planning, programming, project development, evaluation and monitoring purposes;
- Provide the needed GIS technical capabilities and capacities of Network of Network partners and continually update these with the emerging development on ICT; and
- Facilitate access to geographic information and services external to the network.
Whereas, in 2021, a Memorandum of Agreement was forged between the Department of Science and Technology Regional Office No. 2, the Isabela State University, and the National Economic and Development Authority Regional Office No. 2 which geared toward the replication of the Cagayan Valley Regional Geographic Information Network (RGIN) in recognition of the Geoportal’s huge potential in advancing development coordination in all levels and sectors of the government.
Likewise, the adoption of the Cagayan Valley RGIN Innovation Hub by the regions would have a profound impact on the way geographical information is produced, managed, used and shared among different line agencies and local government units as they will greatly benefit from the functionalities and features of the system.
As such, four batches of hands-on training on ArcGIS using Flood Hazard Maps were conducted in 2022 as a strategy for pro-active disaster risk reduction management.

Regional Geographic Information Networks (RGINs) established in different regions in the Philippines
Climate Action plan
The climate change center 5-year strategic plan (2020-2025) through its Vision, Mission, and Goals/Objectives, covers the University Action Plan to address Climate Change through both Adaptation (avoiding exposure to climate-related hazards, reducing affected areas and enhancing adaptive capacities) and Mitigation (GHG emission reduction) are shared with local government and/or local community groups through seminars/lectures during trainings/workshops on formulation of Local Climate Change Action Plans (LCCAP) for the vulnerable communities which had been rolled out since 2020.
Cooperative Planning for Climate Change Disasters
The Disaster Response Operations Monitoring and Information Center (DROMIC) of the Department of Social Welfare and Development-Disaster Response Management Bureau (DSWD-DRMB) conducted a training on Community-based Mapping for Strengthening Disaster Resiliency through Geographic Information System (GIS) for personnel of DSWD-Field Office II and Local Government Units (LGUs) from Region 2 in October 17-21, 2022 at Hotel Andrea, Cauayan City.
The activity aimed to establish a common understanding and basic knowledge on the importance and use of GIS in the collection, validation, integration, and analysis of spatial data obtained from the LGUs and other government agencies for Disaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM) programs, projects and activities.
On the other hand, Isabela State University convened government agencies and international academic partners from Japan in the Stakeholders Forum on Integrated Flood Risk Management in Cagayan River Basin on July 14, 2022.
The forum aimed to strengthen the capacities of policy makers, managers, and practitioners of river basin organizations on flood management through knowledge sharing of new approaches, techniques, methodologies, and good practices from partners here and abroad.
Information and support to local or regional government in local climate change disaster/risk early warning and monitoring
As climate change brings increasing concern on water-related hazards over the years, academic and research groups from the Philippines, Japan, and Vietnam have undertaken a flood and sediment project for the Asia-Pacific Region.
The project dubbed as “Integrated Flood and Sediment Management in River Basin for Sustainable Development (FSMART)” has Isabela State University as a member, closely working with the Kyoto University from Japan and Thuy Loi University in Vietnam.
FSMART would be looking into the impacts brought by climate change and human interventions on reservoir sedimentation, flood inundation, agricultural practices, and river and coastal regions- specifically in the areas of Vu Gia-Thu Bon and the Cagayan River Basins.
As a commitment, Isabela State University has launched the Smart Water Infrastructure Management (SWIM) Research and Development Center in an effort to consolidate water-related research in the University.
At the same time, SWIM R&D sets up a physical facility that would bridge initiatives on water studies in Northern Luzon and the country at large.
Side by side the research center is ISU’s counterpart project for FSMART- the Integrated Flood and Water Resources Management in ASEAN River Basins for Sustainable Development (IFWARM), which is funded by DOST- PCIEERD.

Article from the Asia-Pasific Network for Global Change Research in view of the Integrated Flood and Sediment Management in River Basin for Sustainable Development (FSMART)
Also, a research was conducted which aimed to elucidate a smarter DRRM that worked for LGU Gonzaga, Cagayan through river basin-wide LiDAR-based flood advisory system adhering to Industry 4.0 toward digital transformation and use of exponential technologies such as LiDAR, rain gauge and water level sensors and internet of things (IoT) and the accuracy of a new flooding simulation system based on LiDAR-derived digital terrain and surface models (DTM and DSM) capable of predicting impacts to agriculture, aquatic, forestry and natural resources (AAFNR) and properties at specified rainfall scenarios.
Residential buildings, cultivated areas, and clay loam soils were mostly affected by floods and increased in magnitude as rainfall volume increased/rainfall return period (RRP) became longer. Vulnerable communities in consensus with LGU officials proposed and located in the 100-year flood hazard prevention and mitigation map the following structural and non-structural interventions: 500 capacity barangay and 3,000 capacity municipal evacuation centers, watershed and riverbank protection through 200 ha bamboo and tropical fruits plantation, construction of diversion dam in upland barangays, 30 km sea breaker along coastal barangays, change in planting calendar, livestock raising and flood early warning system using existing rain gauges and automatic water level sensor.
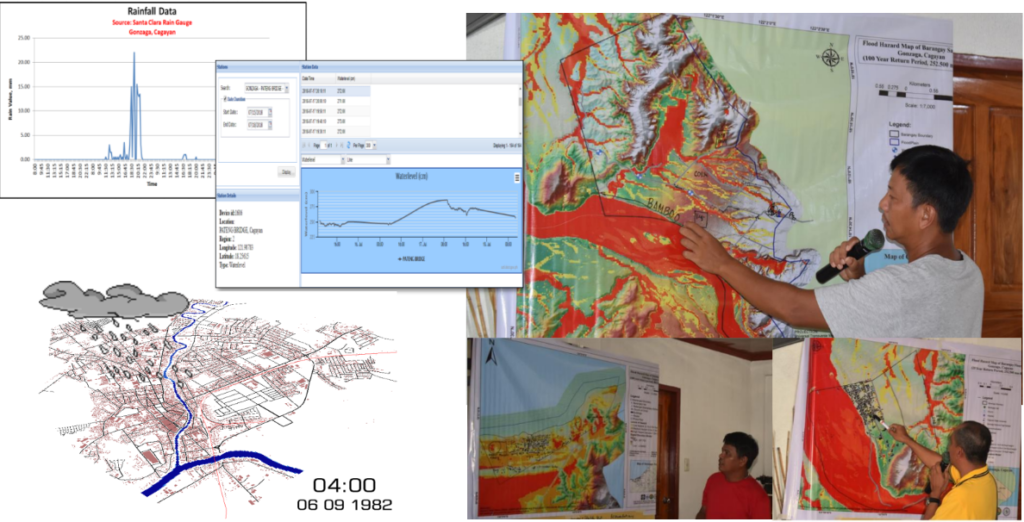
The proponents discussing the LiDAR-based Flood Advisory System in Aunugay River Basin, Gonzaga, Cagayan
Lastly, Project MaHal (Malinis na Hangin Para sa Lungsod): Integrating UP Technologies in Air Quality Monitoring (Project ROAM) in the City of Cauayan integrated different sectors such as the industries, NGOs, LGU, and HEIs. It supported the Smarter City project of Cauayan City. The University forged a MOA with DOST, leading the pilot research and implementation of the Project MaHal.
Collaboration with NGOs on Climate Adaptation
Isabela State University looks to a promising internationalization venture this year as Howest University of Applied Sciences works on partnership with the International Organization for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction Management (IO-CCA-DRRM). The Belgium-based university intends to partner with the international organization for possible academic and research undertakings as revealed in a closed-door meeting between Ms. Katelijne Demeyere, Global Engagement Officer of the Howest Foundation International Office, and Dr. Orlando P. Balderama, ISU Research Vice President.

Dr. Orlando F. Balderama (second person from left in the first picture) together with other ISU personnel and Ms. Katelijne Demeyere, Global Engagement Officer of the Howest Foundation International Office
Also, a partnership between Isabela State University and a South Korean-based company is set to introduce green and sustainable research and development in Cagayan Valley.
ISU and BioGet Incorporated inked an agreement to collaborate for research and tech deployment on Smart Agriculture, Renewable Energy, and Waste-to-Energy Technology System.
With this, ISU and BioGet link the region to the world’s efforts on technologically driven waste disposal, finding means for alternative and renewable energy resources.

ISU officials and BioGet company forged an agreement research and tech deployment on Smart Agriculture, Renewable Energy, and Waste-to-Energy Technology System
Commitment to carbon neutral university
University towards becoming carbon neutral according to the Greenhouse Protocols
In view of the five-year Strategic Plan (2020-2025) of the Isabela State University Climate Change Center, its vision, mission, goals/objectives, and roadmap go hand in hand to continuously develop and implement strategies that will lead the university to be carbon neutral.
These are manifested through the research and extension activities conducted by the different campuses which are considered beneficial for the university and the community.


















